The advent of cloud computing has been transformational for enterprise business computing. No longer do enterprises need to invest time, money and resource on computing hardware, software experts, etc., for delivering products and services to end-users. They can do all these things over the internet by subscribing to any popular cloud computing services like Amazon AWS, Microsoft Azure, etc.
Enterprises normally use any one of the three popular forms of cloud services IaaS, SaaS, and PaaS.
- Cloud Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): Enterprises need to manage applications, data, middleware, and OS.
- Cloud Platform as a Service (PaaS): Enterprises need to manage only application and data; rest is managed by the service provider.
- Software as a Service (SaaS): Enterprises need not manage anything. All they have to do is pay for what they use.
While these are the most widely used types of cloud-based services, the cloud itself is going through fundamental changes to align itself with changing business needs. This evolution has resulted in the cloud taking multiple forms to fit specific business needs best.
Hybrid Cloud
Hybrid cloud, as its name suggests, is the conjunction of on-premise, private and public cloud. It combines the flexibility and scalability of the cloud while promising the security of on-premise servers or private clouds. In a hybrid cloud environment, there is at least one cloud managed by the enterprise itself and one cloud managed by the third party. Enterprises prefer a hybrid cloud environment for matching legacy performance requirements, for strong security of sensitive business data, for greater architectural flexibility. To sum up, a hybrid cloud brings the best of all the three worlds (Public, private and on-premise) to a business computing environment.
Multi-Cloud
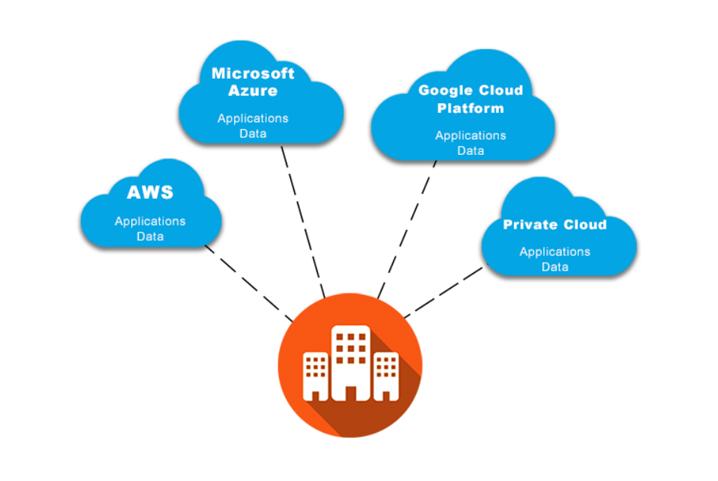
No two service providers offer the same cloud computing solutions from tip to toe. Complementing this diversity of the multiple needs of different business workloads is quite cumbersome. Thanks to this variety in choice, enterprises tend to pick and choose cloud services depending on several diverse factors such as costs, vendor lock-in, downtime by switching between vendors, and last but not least mapping cloud service efficiencies with specific project needs. All these give rise to a multi-cloud business computing environment comprising of AWS, Azure, CGP and much more. On average, an enterprise may use 4-5 cloud services for improving collaborations, efficiency, and productivity.
Edge Computing
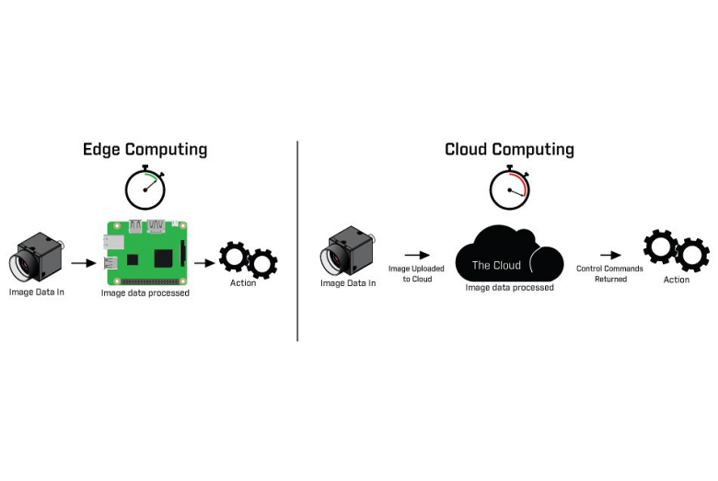
Edge computing is a decentralized form of computing. It is done at the data generating device source itself and offers a business with split-second decision-making capabilities. While edge computing use cases are still limited in the enterprise landscape, its potential impact cannot be ignored. The autonomous vehicle uses edge computing for accurate path planning and vehicle control. The same principles can be applied by enterprises to accelerate data-to-insights journey with edge computing.
Fog Computing
Fog computing is similar to edge computing except for the location of intelligence and computing power. In edge computing, data processing and insight generation is carried out within the device itself. But in fog computing, the location of intelligence and computing power is within the local area network (LAN).
It would be fair to say that evolution in cloud computing is a reflection of the changes in the enterprise landscape. Today, business and technology are inseparably intertwined. The different cloud services and types are only an indication of what enterprise desire and want.
Cloud is changing for the enterprises, and it is perhaps the best time to integrate technology and business together for exploring limitless opportunities for growth and productivity. Are you also planning to move to the cloud? PSI is one of the leading software development companies with over 20 years of experience in implementing enterprise-grade digital solutions. We help enterprises embrace digital transformation with scalable and cost-effective cloud solutions.









