In the previous blog, we explained about EDI (Electronic Data Interchange), this article further focuses on How EDI works and its usefulness for business operations.
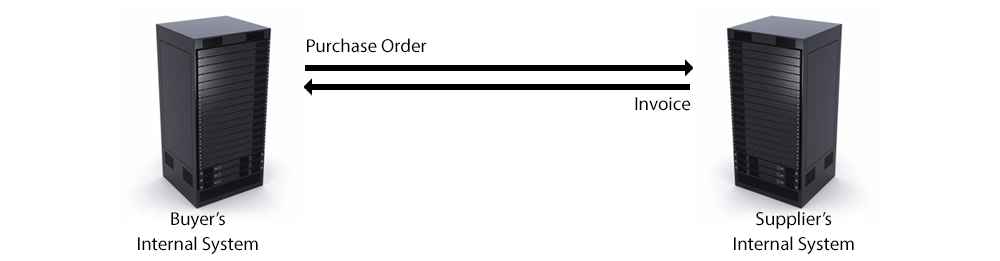
Today EDI is being used in industries like banking, finance, retail, automobiles, etc. to share business documents within the organizations. Exchange EDI document has no involvement of any paper or people, it is directly linked from the sender’s system to the receiver’s system, thus making it faster and cost-effective.
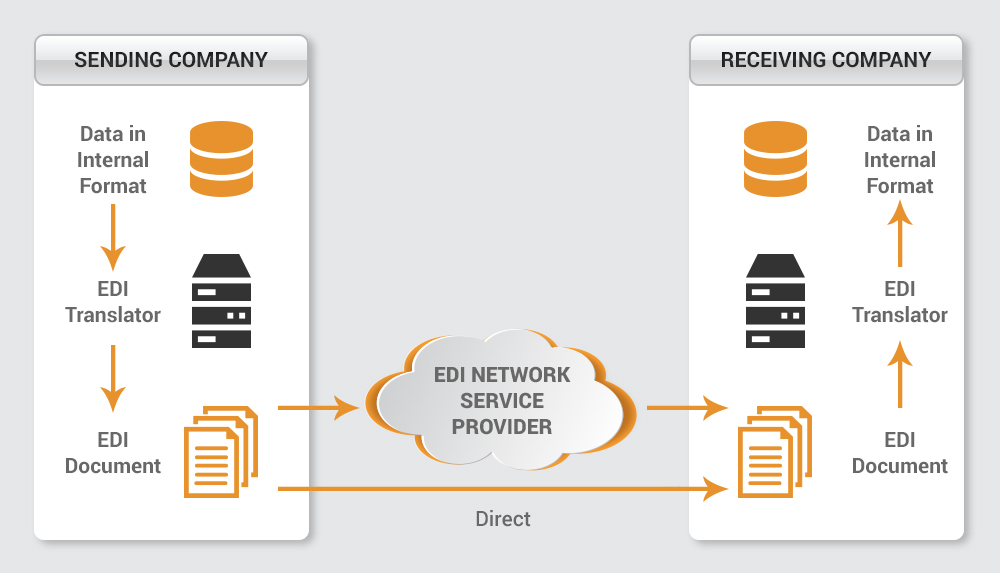
These are the four steps required in EDI document transfer:
- Collect & Create Data File: Identify the data that you want to share in your EDI document. Collect and organize this data. The data can be gathered by direct data entry into the system by people or from some of your existing system. Create a file of this organized data.
- Translate to EDI Document: Translate the collected and organized electronic data file into EDI standard format using appropriate segment and elements. This can be done using EDI translator software. There is three important part of each EDI document i.e., Segment, Data Element, and Envelopes.
- Transfer EDI Document: You can share the documents with your vendor/client once your data file is converted into EDI format. This transmission can directly be done using the Internet or using some provider’s services.
- Receiving End: Once the EDI formatted document is received at the receiver’s end, it is again converted back to a data file using EDI standard format, appropriate segment, and element. This process is done using the EDI translator or services.
EDI Standards
Traditional models for exchanging business exchange is outdated and time-consuming. EDI helps businesses replace old communication bottlenecks with a cost-effective, time-efficient, and paperless alternative. Based on the multiple communication needs of varying business processes and workflows, EDI services supports many standards for processing business documents and information. Some of them are listed below:
- UN/EDIFACT
- ANSI ASC X12 (X12)
- GS1
- ODETTE
- VDA
- HL7
- EANCOM
- HIPAA
- RosettaNet
- SWIFT
- Tradacoms
- VICS
How has been the EDI Impact?
The first and foremost impact of EDI has been paperless business communication. Other business benefits of EDI include:
- Eliminating human error associated with traditional methods of business document storing, organizing, management, and exchange.
- Zero manual entry errors.
- Real-time purchase order and invoice generation.
What Are The Challenges in Implementation?
EDI adoption comes with its unique set of challenges. The primary among these is updating existing business processes for electronic document exchange. This involves the automation of existing business workflows and processes to a certain degree. Most businesses vote against EDI in light of the upfront costs. However, EDI promises a good return of investment once the business process and workflows are aligned with the EDI standard.
EDI Trends in 2021
EDI continues to thrive in the B2B communication realm. But its application in other business processes and workflows is eclipsed by new and innovative technologies like cloud computing. Hence, it is essential to reassess EDI’s place in the current technology landscape, particularly in supply chain ecosystems where it still has reliable adoption rates. Moreover, EDI adoption is expected to get a new lifeline following the Pan European Public Procurement Online (PEPPOL) EDI protocol or the PEPPOL.
EDI will survive as long as supply chain systems around the globe, including key players like Walmart, Amazon, etc. do not make a collective move towards a more efficient digital alternative. PSI’s BPM solutions are tailored to improve existing business processes for stronger collaborations and engagements. Use our custom application development service to automate traditional processes and workflows for business productivity and value. In the previous blog we explained about EDI (Electronic Data Exchange), this article further focuses on How EDI works and its usefulness for business operations.
In the previous blog we explained about EDI (Electronic Data Exchange), this article further focuses on How EDI works and its usefulness for business operations.
Today EDI is being used in industries like banking, finance, retail, automobiles etc. to share business document within the organizations. Exchange EDI document has no involvement of any paper or people, it is directly linked from the sender’s system to receiver’s system thus making it faster and cost effective.

These are the four steps required in EDI document transfer:
- Collect & Create Data File: Identify the data that you want to share in your EDI document. Collect and organise this data. The data can be gathered by direct data entry to the system by people or from some your existing system. Create a file of this organised data.
- Translate to EDI Document: Translate the collected and organised electronic data file into EDI standard format using appropriate segment and elements. This can be done using EDI translator software. There are three important part of each EDI document i.e. Segment, Data Element and Envelopes.
- Transfer EDI Document: You can share the documents with your vendor/client once your data file is converted into EDI format. This transmission can directly be done using Internet or using some provider’s services.
- Receiving End: Once the EDI formatted document is received at receiver’s end, it is again converted back to data file using EDI standard format, appropriate segment and element. This process is done using EDI translator or services.

EDI Standards
There are several EDI standards commonly used. Some of them are listed below
- UN/EDIFACT
- ANSI ASC X12 (X12)
- GS1
- ODETTE
- VDA
- HL7
- EANCOM
- HIPAA
- RosettaNet
- SWIFT
- Tradacoms
- VICS
[:]